Public Key Infrastructure
Public key infrastructure(PKI) is a set of roles, policies and processes which are essential to facilitate Asymmetric key cryptography. PKI allows mapping public keys to users/entities and provides an ability to verify the public key offline.
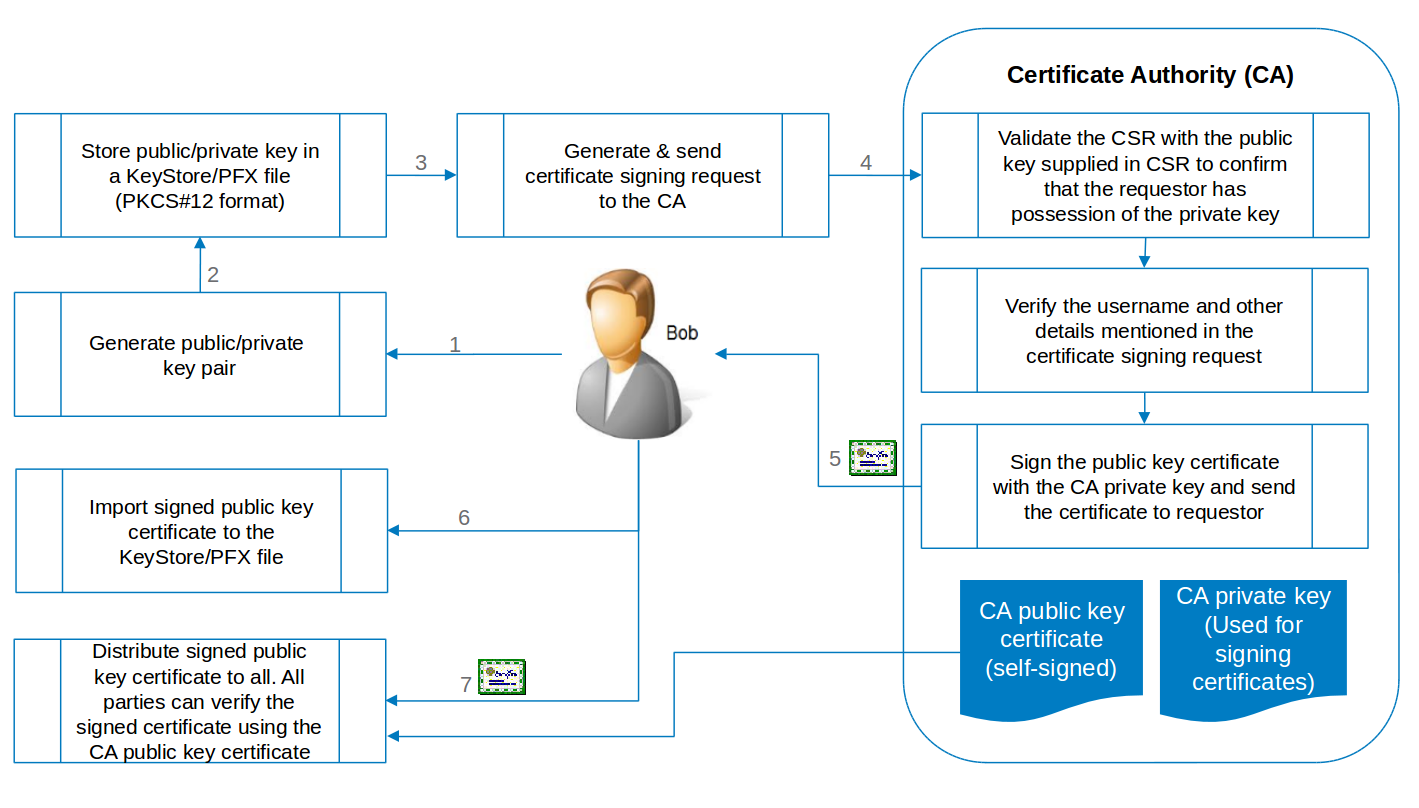
- PKI consists of a certificate authority (CA), which is trusted, and can certify the identity of other users.
- The public key that is to be mapped to a user is packaged into a certificate format (X509 is a popular format) which contains the public key, name of the key owner, organization details and a digital signature from the CA. The packaged format is referred to as a public key certificate.
- The CA accepts public key certificate signing requests(CSR) from users/entities and verifies the authenticity of the certificate requestor through a process.
- A certificate signing request (CSR) is the public key of the requestor signed by the private key of the requestor. The signature in the CSR will be verified by the CA using the public key in the CSR and hence the CA can confirm that the requestor of the certificate has access to the private key corresponding to the public key being certified.
- Once the certificate requestor is verified and found to be the legitimate user and owner of the public/private key pair, the CA signs (digital signature) the public key in the CSR and creates a signed public key certificate.
- All users will also hold the public key certificates of the trusted CAs for validating (the digital signature) other user certificates.